- Introduction
- Maintenance
- Preparation
- Service specifications
- Diagnostics
- 2JZ-GE Engine
- 2JZ-GTE Engine
- 2JZ-GTE Turbocharging
- 2JZ-GE Emission control
- 2JZ-GTE Emission control
- 2JZ-GE SFI
- 2JZ-GTE SFI
- Cooling
- Lubrication
- Ignition system 2JZ-GE
- Ignition system 2JZ-GTE
- Starting system
- Charging system
- Clutch
- W58 manual transmission
- V160 manual transmission
- A340E 2JZ-GE automatic transmission
- A340E 2JZ-GTE automatic transmission
- Propeller shaft
- Suspension and axle
- Brake system
- Steering
- Supplemental restraint system
- Body electrical system
- Body
- Air conditioning system
- Initial conditions
- Engine at normal operating temperature
- Air cleaner installed
- All pipes and hoses of air induction system connected
- All accessories switched OFF
- All vacuum lines properly connected
- SFI system wiring connectors fully plugged
- Ignition timing checked correctly
- Transmission in neutral position
- Tachometer and CO/HC meter calibrated by hand
- Start engine
- Race engine AT 2,500 RPM for APPROX. 180 seconds
- Insert CO/HC meter testing probe AT least 40 cm (1.3 ft) into tailpipe during idling
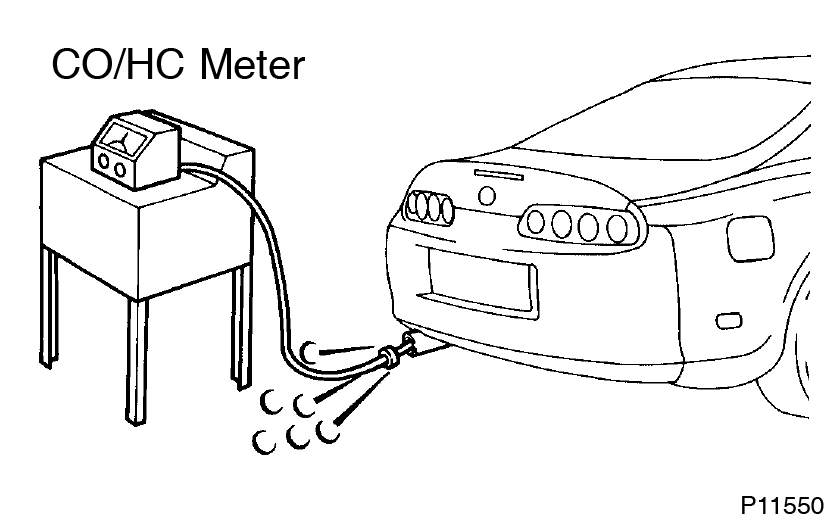
- Immediately check CO/HC concentration at IDLE and/or 2,500 RPM When doing the 2 mode (2,500 rpm and idle) test, follow the measurement order prescribed by the applicable local regulations.
- Check heated oxygen sensors operation. (See page SF-72 )
- See the table below for possible causes, and then inspect and correct the applicable causes if necessary.
| CO | HC | Phenomenon | Causes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | High | Rough idle |
|
| Low | High | Rough idle (Fluctuating HC reading) |
|
| High | High | Rough idle (Black smoke from exhaust) |
|




